Beijing, Dec. 19, 2025 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- In a major advancement for AI model evaluation, the Institute of Artificial Intelligence of China Telecom (TeleAI) has introduced a groundbreaking metric—Information Capacity—that redefines how large language models (LLMs) are assessed beyond traditional size-based comparisons. This new approach reveals that true model “talent” lies not in size, but in how efficiently a model compresses and processes knowledge relative to its computational cost.
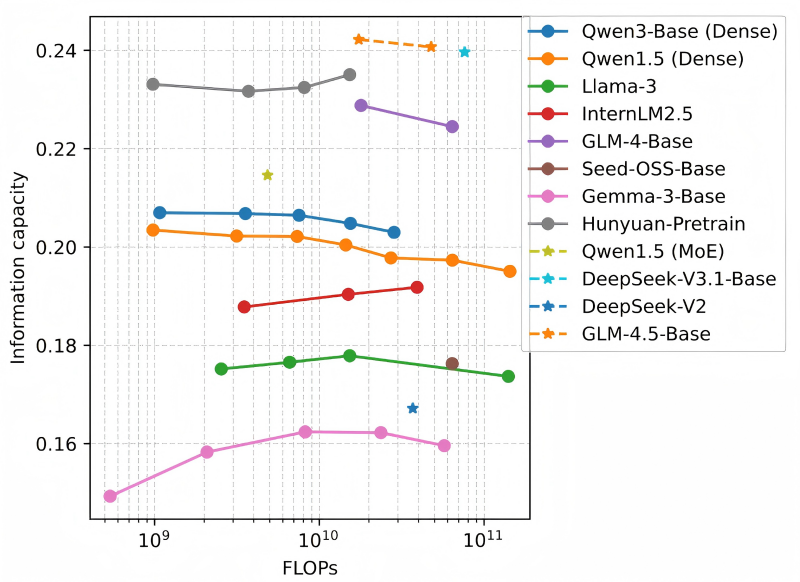
Information capacity is the ratio of model intelligence to the inference complexity, representing the knowledge density inherent in the model. To draw an analogy: if a model is a sponge and information is water, information capacity reflects the sponge’s water absorption efficiency—the more water it absorbs and the faster it does so, the "smarter" the model proves to be. The aforementioned experimental results showed that models of varying sizes within a series exhibit consistent information capacity. Therefore, the metric of information capacity enables a fair efficiency comparison across model series and accurate performance prediction within a model series.
Under the guidance of Professor Xuelong Li, the CTO and Chief Scientist of China Telecom, and the Director of the Institute of Artificial Intelligence of China Telecom (TeleAI) , the research team of TeleAI leveraged information capacity as a metric to evaluate an LLM’s “talent”. Motivated by the strong correlation between compression and intelligence, information capacity quantitatively measures an LLM’s efficiency based on compression performance relative to its computational complexity. It not only reveals the intelligence density produced by a model per unit of computational cost but also facilitates the optimal allocation of computing resources and communication resources under the AI Flow framework.
As inference workloads for large models consume a surging amount of computational resources and energy, accurate evaluation of the inference efficiency has attracted increasing attention from LLM researchers. Via the metric of information capacity, TeleAI has made it possible to evaluate the efficiency of large models across different architectures and sizes. Furthermore, this metric can also effectively guide model pre-training and deployment.
This research not only provides a quantitative benchmark for a greener development of large models but also facilitates dynamic routing of different-sized models for efficient handling of tasks with varying difficulties, which is especially relevant to the Device-Edge-Cloud infrastructure of AI Flow framework. With the rapid evolution of edge intelligence, the "Device-Edge-Cloud" hierarchical network of AI Flow is poised to replace the mainstream cloud-centric computing paradigm in the near future.
To date, all relevant code and data from this research have been open-sourced on GitHub and Hugging Face, empowering the community to collectively advance the standardization of large model efficiency evaluation.
Codebase: https://github.com/TeleAI-AI-Flow/InformationCapacity
Dataset: https://huggingface.co/datasets/TeleAI-AI-Flow/InformationCapacity
Leaderboard: https://huggingface.co/spaces/TeleAI-AI-Flow/InformationCapacityLeaderboard

Ziyao Tang tangzy14@chinatelecom.cn
